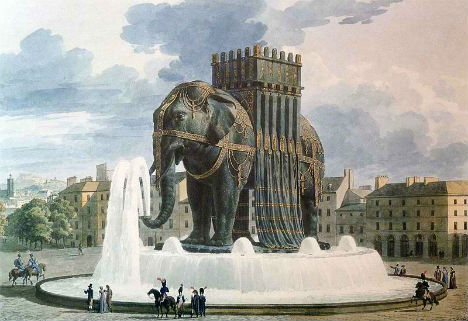The Sydney Opera House might have been little more than a squat concrete building resembling a factory, and a visit to the statue of Abraham Lincoln at the Lincoln Memorial could have required scaling a massive stepped pyramid. Ranging from close second-place finishes in design competitions to proposals that were little more than pipe dreams, these alternative designs for 12 major iconic landmarks around the world represent radical departures from the monuments we’re accustomed to.
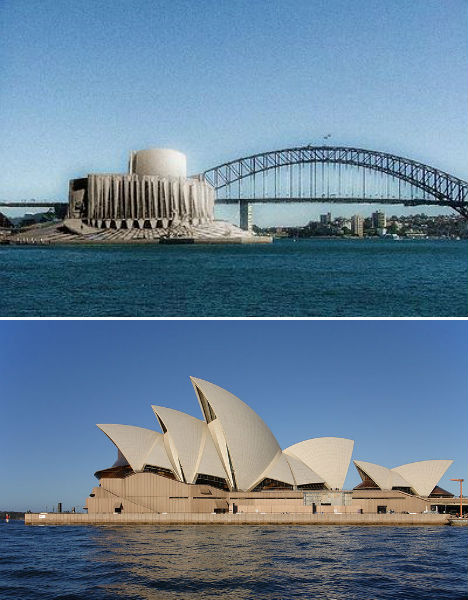
Sydney Opera House
(images via: new world wonders, wikimedia commons)
The Sydney Opera House is one of the most recognizable buildings in the world, with a dramatic series of vaults rising from the ground along Sydney Harbour. But Danish architect Jørn Utzon’s now-iconic design was controversial when it was first proposed in 1957, and the design that came in second place may have been more palatable to the public. American architect Joseph Marzella’s design was rather industrial in its appearance, but didn’t seem quite so out there. It’s hard to imagine the magnificent performing arts venue looking so squat and dull.
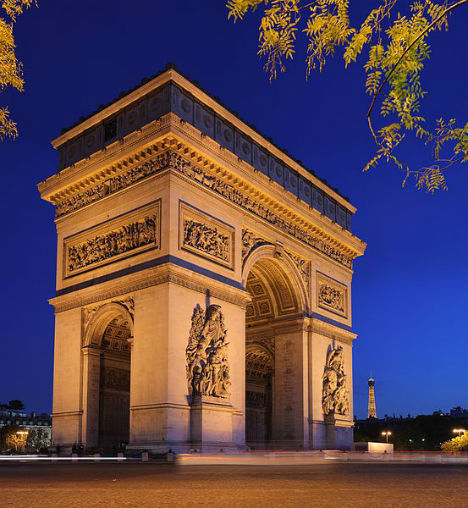
Triumphal Elephant in Place of Paris’ Arc de Triomphe
(images via: wikimedia commons)
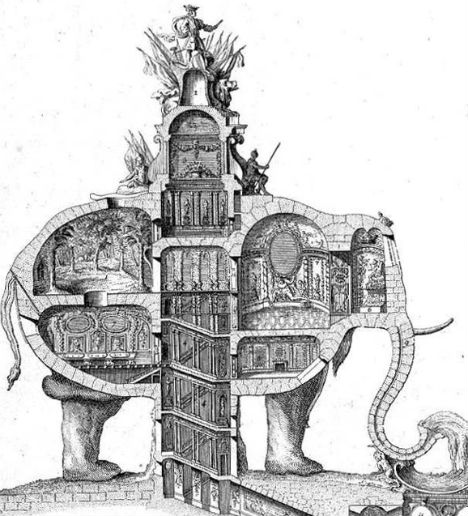
In place of one of Paris’ most famous monuments, the Arc de Triomphe, could have been a three-story elephant monument with a spiral staircase in the underbelly leading to the pinnacle. 18th century architect Charles Ribart offered this monument for the Champs Élysées, complete with a cross-sectional drawing showing the intricate rooms within, but was turned down by the French government.
This isn’t even the only massive, ridiculous elephant statue envisioned for Paris. Originally conceived by Napoleon, the imposing Elephant of the Bastille (third photo) was meant to be cast of bronze and placed in Paris’ Place de la Bastille on the site of the old Bastille prison, which was the birthplace of the French Revolution. A stairway set into the legs would give access to the top, and the base would be surrounded by a fountain. However, only a plaster model was built, as memorialized by Victor Hugo in the novel Les Miserables, and eventually the July Column took its place.
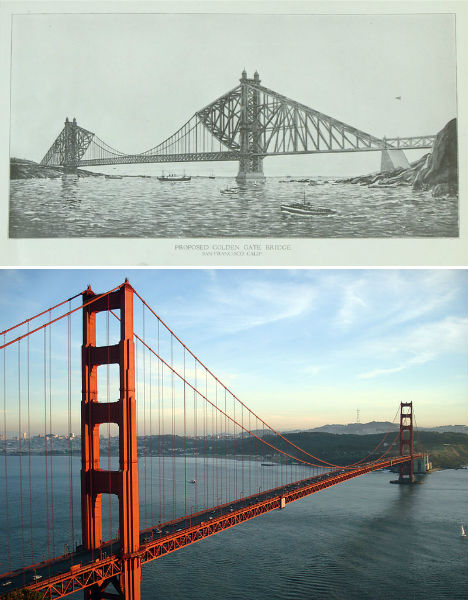
Unbuilt Design for the Golden Gate Bridge
(images via: pbs newshour, wikimedia commons)
Now 76 years old, the Golden Gate Bridge is an iconic symbol of San Francisco, coated in literally millions of gallons of orange paint. The Art Deco-style bridge is one of the longest suspension bridges in the world, beating many experts’ predictions that it wouldn’t last against gale-force winds in the straight where the San Francisco Bay opens to the Pacific Ocean. But this wasn’t engineer Joseph Strauss’ first design. The original proposal is markedly different, with a heavier look combining cantilevered and suspension designs. It was rejected by the planning committee.
Lincoln Memorial Pyramid
(images via: i own the world, wikimedia commons)
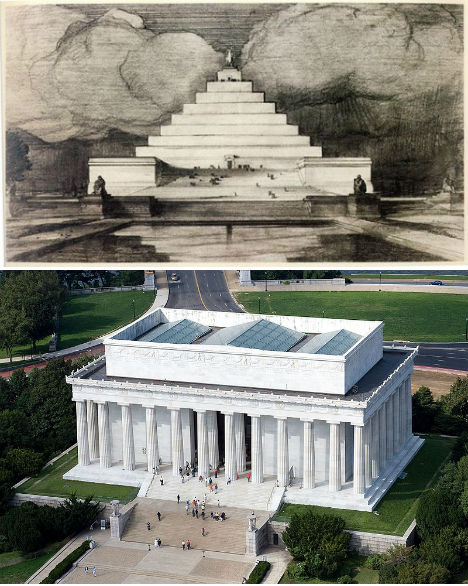
Highlighted at Unbuilt Washington, an exhibition at the National Building Museum in Washington D.C., John Russell Pope’s Lincoln Memorial Proposal replaces the columned rectangular building honoring the 16th president with a pyramid. Anyone who wanted to get up close to Abraham Lincoln’s statue would have had to climb that entire thing to reach it. Some historians believe that this proposal was ridiculous on purpose; Pope wasn’t a fan of the swampy location chosen for the memorial, and may have created this and other absurd designs in an effort to encourage the committee to seek a new setting. Pope went on to successfully design the Jefferson Memorial.
Pyramid Necropolis for London’s Primrose Hill
(images via: andrew gough, wikimedia commons)
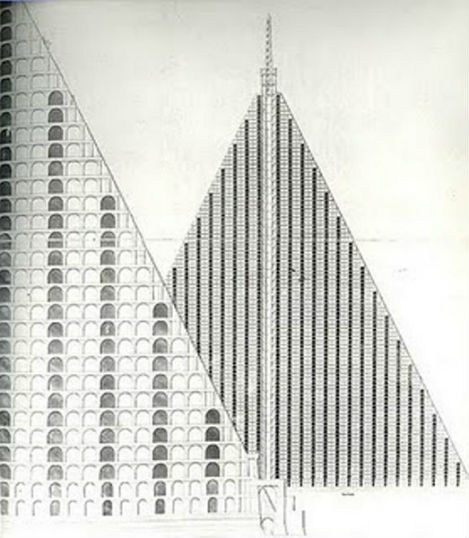
Infused in the Victorian preoccupation with melancholy and inspired by the Egyptian spoils of traveler and tomb-raider Giovanni Battista Belzoni, London architect Thomas Wilson proposed a massive, 15-acre pyramid-shaped necropolis for the city’s Primrose Hill. The granite pyramid would have towered into the air with 94 tiers of tombs in honeycomb shapes and a base measuring 18 acres, casting a gargantuan shadow over the hill many Londoners use for picnics and looking out over the city. Churchyards were so crowded at the time, that graves were bursting out of the ground – but concerns about what to do with London’s dead weren’t enough to convince the public that a necropolis was a good idea.
White House Alterations for President Harrison
(images via: loc.gov, wikimedia commons)
While he’s not nearly as forgettable as his grandfather, ninth United States President William Henry Harrison – who died after just 32 days in office – many Americans will struggle to recall any of twenty-third President Benjamin Harrison’s achievements during his tenure in the White House. However, Harrison could have made quite a mark. The first President to reside in the White House after it was wired for electricity, Harrison and his First Lady, Caroline Harrison, proposed significant changes to the complex that were never carried out. However, ten years later, Theodore Roosevelt made plenty of changes of his own, including the addition of the West Wing.