HOT Hands-On-Technology SmartWatch
Are watches the next big thing in smart phone tech? A lot of companies seem to think so, and this gadget is a frills-free example of what they could do. The HOT Smartwatch is capable of understanding your gestures to make calls, and it’s also able to read and send texts, check status updates, check the weather and perform other functions you’d normally do on your phone. It’ll even automatically send a message to emergency personnel if you fall down and hurt yourself. Prices start at just $109.
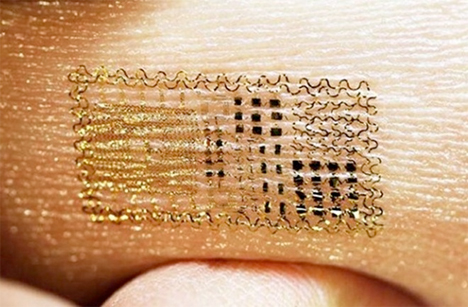
Electronic Stick-On Tattoos Track Body Functions
This ultrathin, self-adhesive electronic ‘tattoo’ could monitor heart rates, brain waves and muscle activity using little to no power, and it’s so unobtrusive the wearer will hardly notice it. The device draws power from electromagnetic radiation or miniature solar collectors, and it’s thinner than the diameter of a human hair. It can stay on the skin for up to 24 hours without any adhesives. It could be particularly helpful for areas of the body that tend to be hard to monitor with conventional equipment, like the throat.
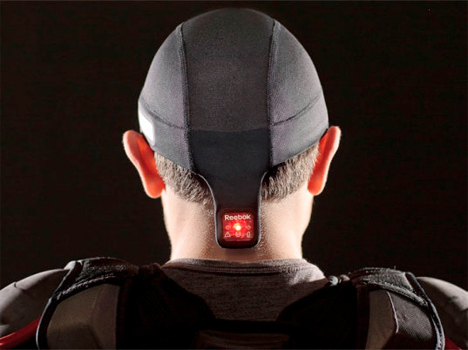
Reebok CheckLight Hat Measures Head Impact Severity for Athletes
The Reebok Checklight is a lightweight cap that measures acceleration and the severity of a hit as athletes take part in practice or games. An indicator light glows green when the hit isn’t dangerous, yellow for a moderate impact and red for a severe impact that requires medical help. It could help medical professionals and athletes learn more about brain injuries sustained in sports, and how they can add up over time. It’s battery-powered, recharges via USB and costs $149.98.
T-Shirt Converts Sound Into Electricity
Tested at England’s Glastonbury Festival when it debuted in 2011, the ‘Sound Charge’ tee contains technology that turns sound waves into enough electricity to power a cell phone or other portable device. It consists of a modified piezoelectric film, which functions like a giant microphone absorbing sound pressure waves. Interlaced quartz crystals convert these acoustic signals into electricity, which is fed into an internal reservoir battery. That means you can keep your phone charged up just by hanging out next to a stage or some speakers.